The Benefits of Automation
In the past, manufacturing and industrial companies implemented only basic instrumentation to run processes and create products, with primary focus placed on effective measurement and reliable control. During this time, material and energy costs could remain fairly stable throughout all processes, and automation was viewed as a mere prerequisite to operations; its value was tied solely to the operations themselves.
But as material and energy costs began to fluctuate more widely, operational efficiency became more of a concern, and companies began seeking the most energy- and material-efficient production processes available. Automation came to the forefront, and no longer was its value tied only to operations; now it was tied directly to profits.
Allowing for maximized throughput and reduced energy and material consumption, automation is now being used across a wide range of industrial and manufacturing sectors to ensure optimal production safety, efficiency, and value.
Types of Automation Technology
Below are three of the most popular business process automation (BPA) methods.
- Extending an existing IT system — Expanding upon automation already in place can be highly convenient and often seems very cost-efficient upfront, but integrating new components can be costly, and training employees to use the updated system can be extremely time-consuming.
- Purchasing process-specific BPA software — Programs with ready-made, process-specific tools can reduce or even eliminate the need for bringing in IT to assist with implementation and in-house tool development. However, not all industries are able to make use of all available built-in features, while other sectors may require functionalities that are not available — making this a potentially cost-inefficient solution for many companies.
- Purchasing adaptive BPA solutions — Adaptive BPA solutions are essentially a combination of the two methods listed above; using this method, companies purchase new, highly customizable process automation software while also making use of their existing infrastructure in order to create highly efficient, application-specific solutions.
The Advantages of Automation
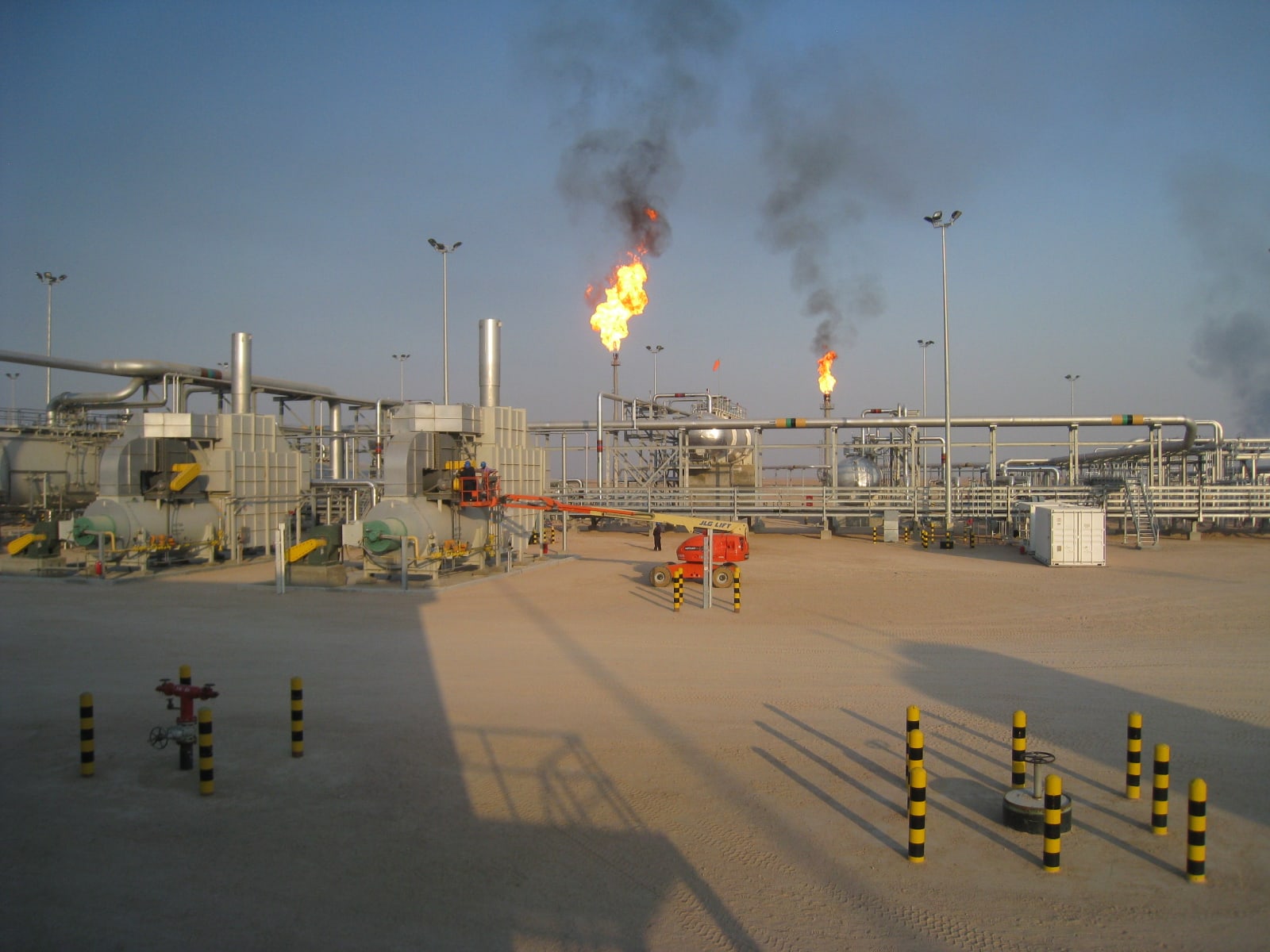 Automation offers a range of benefits for all types of industries and applications. For instance, throughput can be efficiently maximized with job scheduling software that automates production batches, thereby eliminating lag time between jobs and reducing the need for operator intervention. Once a job schedule is determined, automation software operates in a precise sequence, eliminating the risk of operator errors. This naturally increases productivity and reliability, as jobs cannot be forgotten or run out of sequence.
Automation offers a range of benefits for all types of industries and applications. For instance, throughput can be efficiently maximized with job scheduling software that automates production batches, thereby eliminating lag time between jobs and reducing the need for operator intervention. Once a job schedule is determined, automation software operates in a precise sequence, eliminating the risk of operator errors. This naturally increases productivity and reliability, as jobs cannot be forgotten or run out of sequence.
Automation also minimizes energy and material consumption with the same precision that enables flawless scheduling, allowing for significant cost savings and streamlined operations. And, when recovery systems are automated, there is reduced risk of accidental damage to operating systems due to human error. Allowing for environmentally friendly operations and enhanced reliability, automation has proven to be highly effective in preventing failure and maintaining smooth production processes.
Since the economic impact of failure can be easily calculated, it’s equally easy to pinpoint the potential cost benefits of implementing a BPA system. But, since determining the risk of failure is probabilistic, industrial companies are less likely to consider failure-event prevention a valid economic benefit of automation. This is why throughput, energy, and material consumption are the main factors used to measure the overall value of automation systems.
It’s also worth noting that, like any other piece of equipment, automation systems can become outdated, leading to decreased efficiency and higher costs. Regular upgrades will allow for consistently high return on investment (ROI) while ensuring optimal safety and operations, as well as a smaller environmental footprint.
The Disadvantages of Automation
BPA does have its downsides, however. For instance, employees are often resistant to change, and a new automation system could be easily misconstrued as a complete replacement for manual labor. And even if they don’t resist the change, training a workforce to properly implement automation systems can be time-consuming and challenging.
To deal with these issues, first reassure employees that automation still requires human presence and operation, and that their role will actually be more specialized after the introduction of automation equipment; in many instances, this may even mean higher wages. Also, the reduced interaction between humans and machines means fewer injuries and less time lost on the job. That said, some reduction in staff will likely be necessary.
The initial costs involved in adopting BPA may seem counterintuitive at first, especially for companies resistant to change, but the long-term cost and energy savings far outweigh any initial roadblocks.
Automation Solutions From Sigma Thermal
 Sigma Thermal Automation is proud to offer customized automation solutions for clients across a wide range of industries and applications, and our skilled engineers, designers, programmers, and fabricators can meet all types of project specifications and requirements — no matter how complex.
Sigma Thermal Automation is proud to offer customized automation solutions for clients across a wide range of industries and applications, and our skilled engineers, designers, programmers, and fabricators can meet all types of project specifications and requirements — no matter how complex.
Sigma Thermal also offers sophisticated multiple burner management systems (BMS) and combustion control systems (CCS) to accommodate various customer requirements and environmental conditions in the industrial and manufacturing sector.
Comprehensive field service is available for all new and existing installations (even for other company’s equipment). Our expert technicians can provide the following services:
- Firmware upgrades and system configuration
- Process tuning, optimization, and validation
- Network configuration and setup
- Programming and troubleshooting
- Commissioning and training
We also hold the following certifications and compliances:
- ISO 9001:2015
- S. and international certified hardware (CE, UL, FM, CSA, ANSI, ATEX, IEC, etc.)
- S. and international compliant system design (CE, FM, NFPA, and CSA, IEC, ISA, API, SIL)
To learn more about our automation solutions or discuss how we can help with your next project, reach out to the team today.






